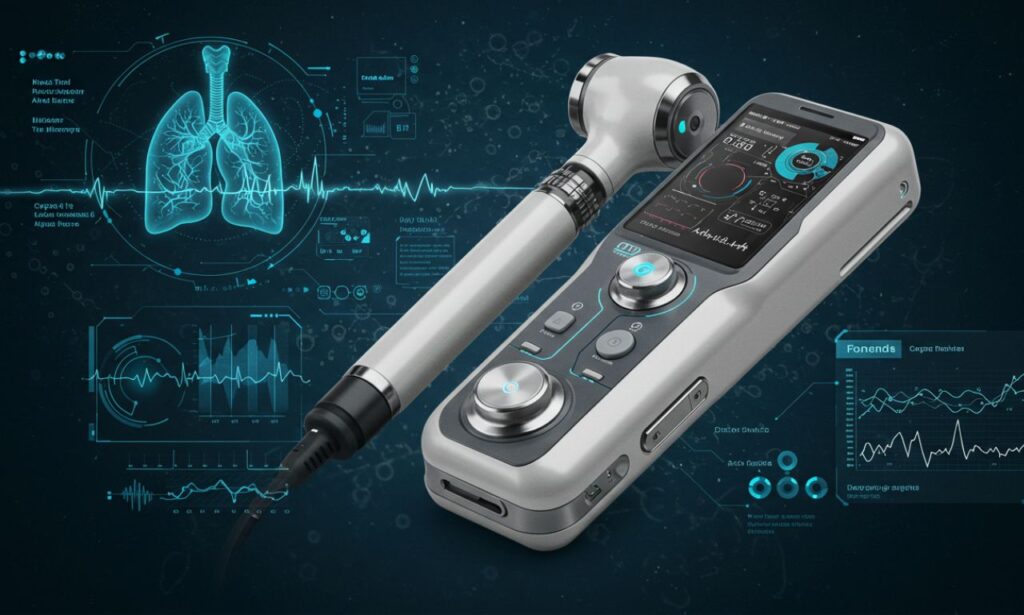
Fonendi represents the next step in medical auscultation—a combination of sound engineering, digital tools, and clinical insight. In simple terms, Fonendi is a smart stethoscope (or phonendoscope) that elevates how healthcare providers listen to hearts, lungs, and internal body sounds. It blends acoustic tradition with modern tech: AI, wireless connectivity, recording, even remote diagnostics. In this article, we explore what Fonendi is, how it works, where it’s used, its benefits, challenges, and its future in modern healthcare.
Fonendi: What It Is Exactly
Fonendi is a modern diagnostic instrument that improves on the traditional stethoscope. It captures internal body sounds—heartbeats, breathing, bowel sounds—with better clarity, and often adds features like amplification, noise reduction, digital recording, and connectivity. Unlike an older analog tool, Fonendi is designed for precision in both quiet and noisy environments.
Etymologically, the name “Fonendi” seems derived from “phonendoscope” or “phonendo-” (sound inside) plus tech branding to suggest modernity. In many sources, Fonendi is described as a device or system bringing together acoustics, electronics, and software to support healthcare diagnosticse.
Fonendi: Evolution of Auscultation Devices
Over more than two centuries, medical listening devices evolved from simple wooden tubes to modern electronic tools. Fonendi reflects that evolution:
-
Early stethoscopes were simple tubes (Laennec’s invention) enabling physicians to listen without pressing their ears directly on the chest.
-
Binaural stethoscopes with flexible tubing improved sound transmission and comfort.
-
Electronic stethoscopes later added amplification, some filtering of interference, recording, and connective.
-
Fonendi adds more advanced components: AI-driven sound analysis, wireless data transfer, mobile app integration, visual displays, sometimes cloud storage.
Fonendi: Key Features and Technology
Fonendi tools generally include several modern features that distinguish them from simpler stethoscopes:
-
High-fidelity sensors that pick up a broad frequency range, including faint murmurs or subtle lung sounds.
-
Noise cancellation or filtering to reduce ambient sound, improving clarity in busy wards or during home visits. Digital amplification so very soft internal sounds are more easily heard.
-
Wireless connectivity / Bluetooth / app integration enabling transmission of sound, visualization of waveform, sharing with other clinicians remotely.
-
Recording and storage so sounds can be saved, reviewed, compared over time, or used for teachin
-
AI or algorithmic analysis in some models, aiding detection of abnormalities or flagging signs that require attention.
Fonendi: Applications in Clinical Practice
Fonendi is useful in many medical settings. Some of its applications:
-
Cardiology: Detecting heart murmurs, irregular rhythms, early valve problems with better sensitivity.
-
Pulmonology: Identifying wheezing, crackles, breath sound abnormalities for conditions like pneumonia, COPD, asthma.
-
Pediatrics / Neonatology: Smaller, gentler versions track lung/heart sounds in infants with high sensitivity.
-
Remote and Rural Healthcare: Allows clinicians to diagnose or monitor patients remotely; smaller clinics benefit when advanced diagnostic imaging is not readily available.
-
Medical Education: Students can learn from recordings, replay unusual sounds, compare classes of pathologies.
Fonendi: Benefits to Doctors, Patients, and Healthcare Systems
Fonendi offers several compelling advantages:
-
Improved Diagnostic Accuracy – enhanced sound quality plus AI helps reduce missed or misinterpreted findings.
-
Efficiency – faster examinations, less guesswork, possibly fewer unnecessary tests.
-
Remote Access – enables telemedicine and remote consultation by sharing sounds and visuals.
-
Patient Monitoring Over Time – stored recordings allow tracking of changes over days or months.
-
Training and Education – better tools to teach auscultation, more examples, repetition.
-
Cost-Effectiveness in Long Term – although initial costs may be higher, gains in efficiency, fewer diagnostic errors, less redundant work may offset that.
Fonendi: Challenges and Limitations
While promising, Fonendi is not without challenges:
-
Cost and Access – advanced models with AI, connectivity, and high-quality sensors cost more than basic stethoscopes; may be less accessible in low-resource settings.
-
Data Privacy & Security – recording, transmitting, and storing sensitive patient data raises concerns; platforms must comply with health data laws.
-
Training & Interpretation – clinicians must learn both to use devices and to interpret AI-aided signals or waveforms appropriately.
-
Reliability and Maintenance – batteries, sensors, software updates, hardware durability are all points of failure.
-
Regulatory Approvals – medical device regulations differ between countries; some Fonendi models must undergo rigorous testing.
-
Overreliance on Technology – risk that clinicians depend too much on AI, potentially undermining clinical judgment if algorithms err.
Fonendi: Real-World Case Scenarios
To see Fonendi in action, consider these hypothetical or reported use-cases:
-
A rural clinic where a health worker uses to record a child’s lung sounds, sends to a pediatric specialist in another city, who diagnoses pneumonia earlier than would otherwise be possible.
-
In cardiology wards, Fonendi helping detect a soft murmur in a patient, then comparing recordings over weeks to see progression.
-
Telemedicine consultations where patient at home uses a device connected to their smartphone; the doctor listens remotely and guides examination.
-
Medical schools using Fonendi devices to expose students to rare lung or heart sounds via recordings and replay, improving learning.
Fonendi: Best Parctices for Usage
To get the most from Fonendi:
-
Ensure proper cleaning and disinfection after each use.
-
Keep firmware / software up to date so AI models, connectivity, and bug fixes are current.
-
Train users in both sound interpretation and device handling.
-
Use in appropriate contexts—quiet enough settings help; background noise still reduces clarity even with noise filtering.
-
Store recordings responsibly, with secure storage and proper patient consent.
Fonendi: Future Prospects and Innovations
What lies ahead for and similar smart auscultation tools:
-
Improved AI Models trained over more varied populations, more sound libraries, better detection of rare conditions.
-
Integration with Wearables so continuous monitoring becomes possible (e.g. patches, smart garments).
-
Remote-only Diagnostics where patients self-record or with minimal assistance, share data with clinicians revising treatment without needing clinic visit.
-
Personalized Sound Profiles allowing baseline sound patterns per patient to help detect deviations more precisely.
-
Cost Reduction making advanced tools affordable and accessible in developing regions.
-
Regulatory Standardization globally so quality, safety, and privacy are ensured.
Conclusion
Fonendi is more than an upgrade—it signifies a shift in how internal body sounds are heard, analyzed, and acted upon. It fuses traditional auscultation with modern technology: AI, connectivity, recording, analytics. The benefits are many—better diagnostics, remote care, education, and more responsive healthcare. Yet, it also brings responsibilities: ensuring privacy, training, cost fairness, and careful interpretation.
If healthcare is to become more precise, more accessible, and more patient-centered, tools like will play a central role. They help us not just listen, but understand. The sound of health is no longer just what we hear—it’s what we can analyze, act on, and improve.